Kidney Stones vs UTI: Understanding the Overlapping Effects and Therapy Techniques
Kidney Stones vs UTI: Understanding the Overlapping Effects and Therapy Techniques
Blog Article
Comprehending the Key Differences Between Kidney Stones and Urinary Tract Infections: A Thorough Summary for Patients
Understanding the distinctions in between kidney stones and urinary tract infections (UTIs) is necessary for people who may be experiencing comparable symptoms yet encounter greatly various health and wellness obstacles. As we discover these crucial aspects, it comes to be clear that acknowledging the unique attributes of each condition can exceptionally impact patient results.
Introduction of Kidney Stones
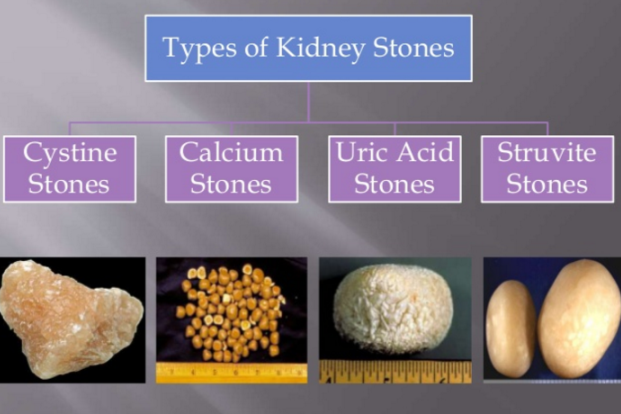
The development of kidney stones, a excruciating and commonly debilitating condition, highlights the important significance of maintaining renal health and wellness. The primary types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with distinct causes and threat factors.
Several aspects add to the formation of kidney stones. Dehydration is a considerable risk, as insufficient liquid consumption can cause concentrated pee, advertising crystal formation. Nutritional routines, consisting of high sodium and oxalate usage, can worsen the threat. Additionally, metabolic disorders and specific medical problems may incline individuals to stone development.
Signs of kidney stones can consist of severe flank queasiness, hematuria, and pain, which frequently trigger urgent clinical examination. Treatment alternatives vary, varying from increased fluid consumption and nutritional adjustments to clinical interventions such as lithotripsy or medical removal, depending upon the dimension and place of the stones. Comprehending these aspects is important for efficient avoidance and monitoring.
Introduction of Urinary System System Infections
Urinary system infections (UTIs) stand for a common yet significant wellness concern, influencing millions of individuals every year. These infections occur when germs get in the urinary system, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The bulk of UTIs are triggered by Escherichia coli, a kind of bacteria generally discovered in the stomach system. While UTIs can affect any individual, they are specifically common in females due to anatomical differences that assist in bacterial entrance.
The threat elements for developing a UTI include sex-related task, particular kinds of birth control, urinary system retention, and a history of previous infections. Straightforward UTIs are usually restricted to the bladder and are more common in healthy individuals, while difficult UTIs might entail the kidneys and take place in those with underlying health and wellness issues.
Trigger medical diagnosis and treatment are necessary to protect against difficulties, such as frequent infections or kidney damages (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Typically, UTIs are treated with antibiotics, and preventative procedures can be employed for those with regular events
Typical Signs Contrast
Signs and symptoms of urinary system system infections and kidney stones can often overlap, causing complication in medical diagnosis. Both conditions can present with pain in the lower abdomen or back, yet the nature and place of the pain often differ. In urinary tract infections (UTIs), clients commonly experience a burning feeling throughout peeing, frequent prompts to urinate, and strong-smelling or gloomy pee. On the other hand, kidney stones have a tendency to cause extreme, acute pain that radiates from the back to the reduced abdominal area and groin, usually defined as colicky discomfort.
In addition, UTIs may be come with by high temperature and cools, particularly in much more serious cases, while kidney stones can lead to nausea or vomiting and throwing up because of intense pain. Both problems can result in blood in the pee (hematuria), but the presence of blood is much more commonly related to kidney stones. While pain during peeing is a characteristic of UTIs, kidney stones commonly present with more severe pain episodes, which may go and come. Comprehending these signs and symptom distinctions can aid individuals in acknowledging their condition, although medical examination stays necessary for accurate medical diagnosis and treatment.
Medical Diagnosis Methods
How can healthcare professionals precisely distinguish in between kidney stones and urinary tract infections? The analysis procedure starts with an extensive case history and a comprehensive evaluation pop over to this web-site of the patient's signs. Clinicians usually carry out a physical assessment, which might expose tenderness in the abdominal area or flank area, guiding the diagnostic path.
Lab examinations play a crucial function in comparing these 2 problems. Kidney Stones vs UTI. A urinalysis can identify the existence of blood, crystals, or germs, which are a measure of either condition. In cases of urinary tract infections, the urinalysis might reveal a considerable existence of leukocyte and nitrites, while kidney stones may present with particular crystals
Imaging studies, such as abdominal ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) checks, are vital for imagining kidney stones. These imaging methods allow doctor to analyze stone dimension, location, and potential blockages in the urinary system tract. In comparison, urinary tract infections usually do not require imaging unless problems are believed.
With each other, these diagnostic techniques empower healthcare professionals to precisely distinguish and diagnose between kidney stones and urinary system infections, guaranteeing that people obtain appropriate care and management.
Therapy Options and Avoidance
While both kidney stones and urinary system system infections (UTIs) call for timely therapy, their monitoring strategies vary substantially.
The therapy for kidney stones typically entails pain monitoring, hydration, and in many cases, medical procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or ureteroscopy to break or get rid of down stones. Patients are regularly suggested to enhance liquid intake to facilitate stone flow and minimize recurrence. Dietary modifications may likewise be needed, depending upon the stone type.
On the other hand, UTIs are primarily treated with prescription antibiotics to eliminate the microbial infection. The details antibiotic prescribed depends on the germs recognized and neighborhood resistance patterns. Added procedures, such as enhanced fluid consumption site link and urinary analgesics, might help ease signs.
Prevention methods vary as well; for kidney stones, keeping ample hydration and sticking to nutritional restrictions can be effective. For UTIs, preventive strategies include proper health techniques, peing after sexual intercourse, and perhaps prophylactic anti-biotics for recurring infections. Comprehending these treatment and avoidance techniques is essential for efficient monitoring and to minimize the risk of problems related to both problems.
Verdict

Comprehending the differences in between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is essential for individuals that might be experiencing comparable symptoms yet face significantly various health and wellness challenges. The primary kinds of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with unique reasons and risk factors.
Report this page